Article by Emanuela Mari.
After well over two years of renovations, the Great Hall of the Months in Ferrara’s Palazzo Schifanoia, one of the most extravagant and fascinating residences of the Italian Renaissance, has reopened to the public gaze. Borso d’Este commissioned a group of local artists to complete the celebrated fresco cycle that decorates its walls in 1469. The careful restoration, complemented by the new and much-improved lighting, has given it new life.
Borso d’Este was an illustrious member of Ferrara’s Este family, which ruled over the city for around 400 years from the 13th Century. He was very fond of sumptuous and magnificent displays of grandeur, which he used to great success to impress his subjects as well as neighbouring States. He wasn’t alone in this type of exercise: it was common in most Renaissance courts, where culture and shows of magnificence were often used as a political tool.
The fresco cycle of the months on the walls of Palazzo Schifanoia’s Great Hall is a result of these attitudes. The whole palace itself is a celebration of leisure and frivolous diversion as the name of the palace suggests — Schifanoia derives from the court’s use of the palace to avoid boredom (schifar la noia). It was also used to entertain and house foreign dignitaries and important guests.
The artwork is an enormous calendar that represents and glorifies the good acts and positive outcomes of Borso d’Este’s government. These are set out month-by-month and are depicted as being influenced and protected by the classical divinities and the stars according to the medieval astrological tradition.
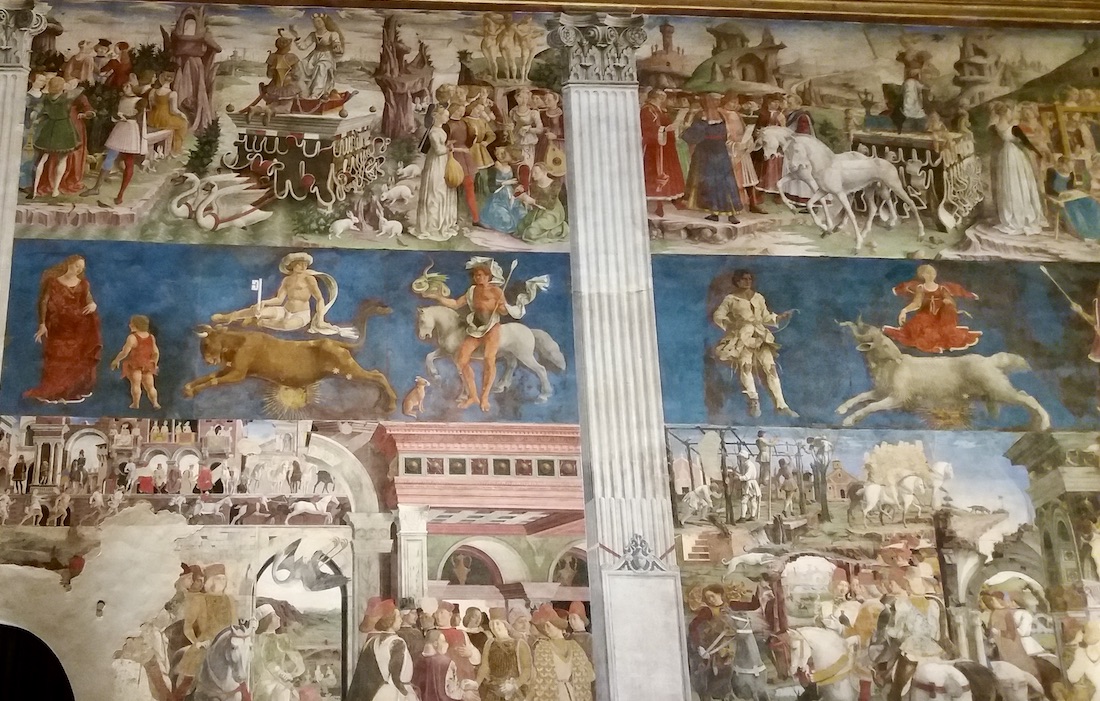
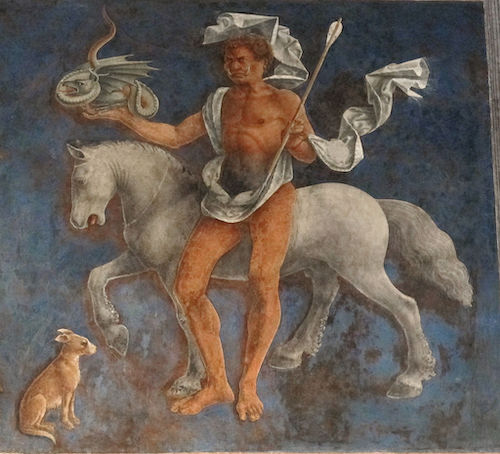
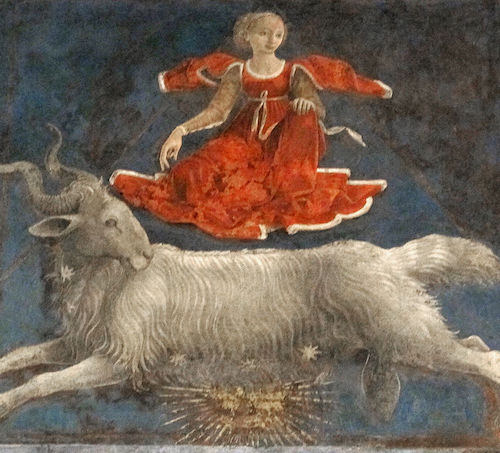
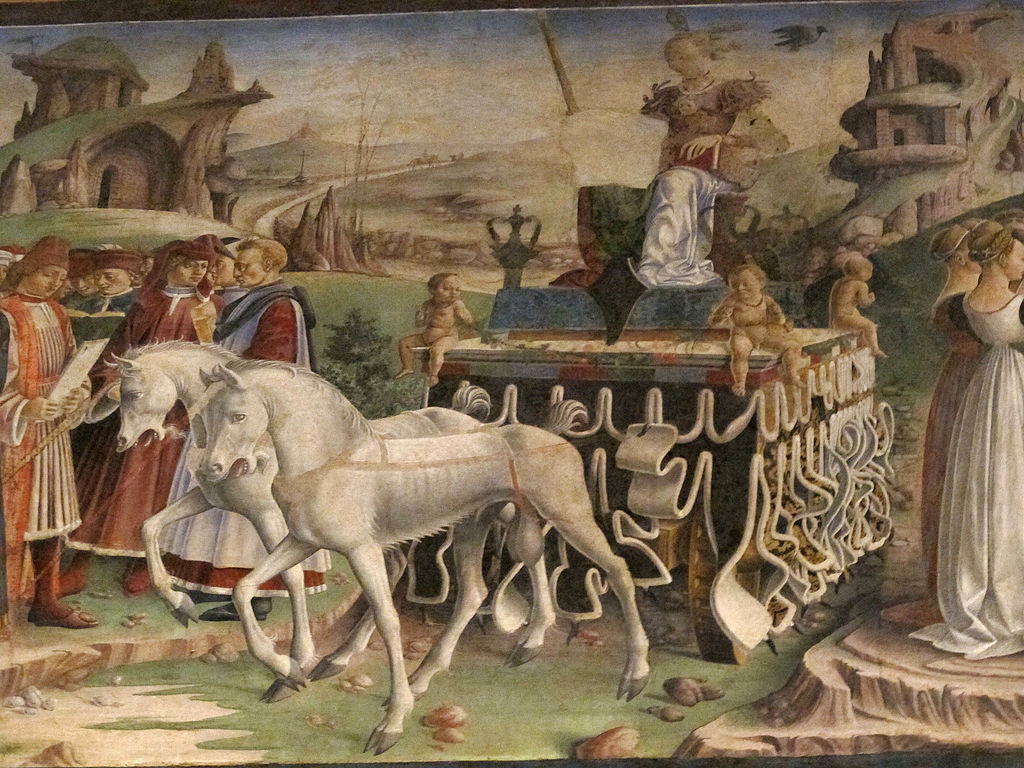
The fresco portrays a loggia in the foreground with various scenes playing out behind it. The columns of the loggia frame the months, and each frame is divided horizontally into three sections. The top section portrays one of the classical divinities (on a triumphal float surrounded by followers and proteges). The middle is an astrological representation, with the sign of the Zodiac, surrounded by the three patrons of that month according to an Arabic reading of astrology and magic. The bottom section depicts scenes of Borso d’Este surrounded by his court, busy with the activities of government and court life, such as hunting with falcons.
Detail from the month of March by Francesco del Cossa – The Triumph of Minerva
Image by Sailko / CC BY-SA and found on Wikimedia Commons
The details of the frescos are so intricate and astounding that the meaning of some, especially in the middle section, are today shrouded in mystery. The fresco cycle, with its sophisticated and complex iconographic language, was conceived by the great Pellegrino Prisciani, Borso d’Este’s court intellectual. He was an important and influential figure in the cultural scene of the Ferrara court, an all-round humanist, well-versed in many disciplines, including astrology.
As for the artists and their work, they were a very talented group that created one of the most extraordinary works of art of the Renaissance. There is one artist in particular whose talent stands out from the rest. Francesco Del Cossa’s superior technique and exceptional artistic style make his contribution to the hall’s Eastern wall the most impressive. His work has survived the test of time much better than that of his colleagues.
Francesco Del Cossa is one of the most noteworthy, yet forgotten artists of the 15th Century. We know very little about his formative years. What we do know is that he worked between Ferrara and Bologna and that he was sought-after and much respected by his contemporaries and peers, including Michelangelo. So much so, that his work inspired an important school of followers.
As a final note, a warning to the prospective visitor. Unfortunately, not all of the fresco cycle has survived intact. If Del Cossa’s work on the Eastern wall (the months of March, April and May) is still in exceptional shape, and that of various masters (June to September) on the Northern wall is well maintained, the same cannot be said about much of the rest, where only faint traces of the old decorations remain. This is in part due to the ravages of time and partly because the fresco was painted over and forgotten for centuries.
In 1598, when the Este could not provide a direct line of succession, the Pope, who had granted the Este feudal rights to Ferrara, expelled them from the city and annexed it to the Papal States. Palazzo Schifanoia like the majority of the more than 50 leisure residences interspersed throughout the territory, fell into decay.
The Este’s expulsion brought to an end an era of fervid artistic activity and arguably the most prosperous period in Ferrara’s history. Their court was considered one of the most refined and progressive in all of Europe. They left the city of Ferrara a fantastic blueprint to their Ideal City they had cultivated for centuries, echoes of which are still evident today. The fresco cycle of the months in Palazzo Schifanoia is a magnificent example of this.
We visit Ferrara on our Undiscovered Riches – Discovering Emila Romagna tour, next scheduled for September 2021 and Emanuela will take us on a guided visit to the Palazzo Schifanoia.
Thank you to Emanuela Mari, local tour guide from Ferrara for contributing this article.
Emanuela fell in love with her city from a very early age — its art, history and culture were so intriguing that she decided to turn it into a career. She first completed a humanities degree (Lettere Moderne) at the University of Ferrara. She then undertook additional studies to become a licensed tour guide for the province.
She’s been working as a tour guide for more than twenty years and loves introducing her clients to Ferrara and its treasures. She speaks Italian, French and English fluently.
If you’re thinking of visiting Ferrara once this pandemic is over, you should definitely book a guided tour of Palazzo Schifanoia with her! You can contact her via her Facebook page, or of course, through us.